Did you know that nearly 70% of credentials used today are still paper-based or PDF files — both of which can be easily forged, lost, or take forever to verify?
In this modern age of AI, proving the authenticity of digital credentials and documents is tougher than ever. We no longer know what's real anymore. This is a global problem. We constantly worry about our data being stolen and misused. We all want a world that feels safe and trustworthy again.
Now, let's look at what Verifiable Credentials (VCs) are — and how they can help mitigate these issues by building a secure, trusted digital ecosystem where users truly own their credentials, not the system.
A Verifiable Credential is a digital attestation that can be cryptographically verified to ensure its authenticity and integrity. It contains verified information about a person, organization, or asset.
Key features of Verifiable Credentials include tamper-proof security, global verifiability, and user privacy and control. Examples of such credentials include academic degrees, professional licenses, and identity documents, among others. These credentials can be issued by universities, certification bodies, and organizations.
Verifiable Credentials (VCs) are stored in a digital wallet, giving users full control over their credentials — whether stored on mobile, cloud, or other secure wallet platforms.
How It Works
The model that explains how Verifiable Credentials (VCs) work is called the Trust Triangle, which consists of three main participants:
Issuer: The entity that issues and can revoke credentials.
Holder: The individual or organization that owns and presents the credentials.
Verifier: The party that validates and verifies the credentials.
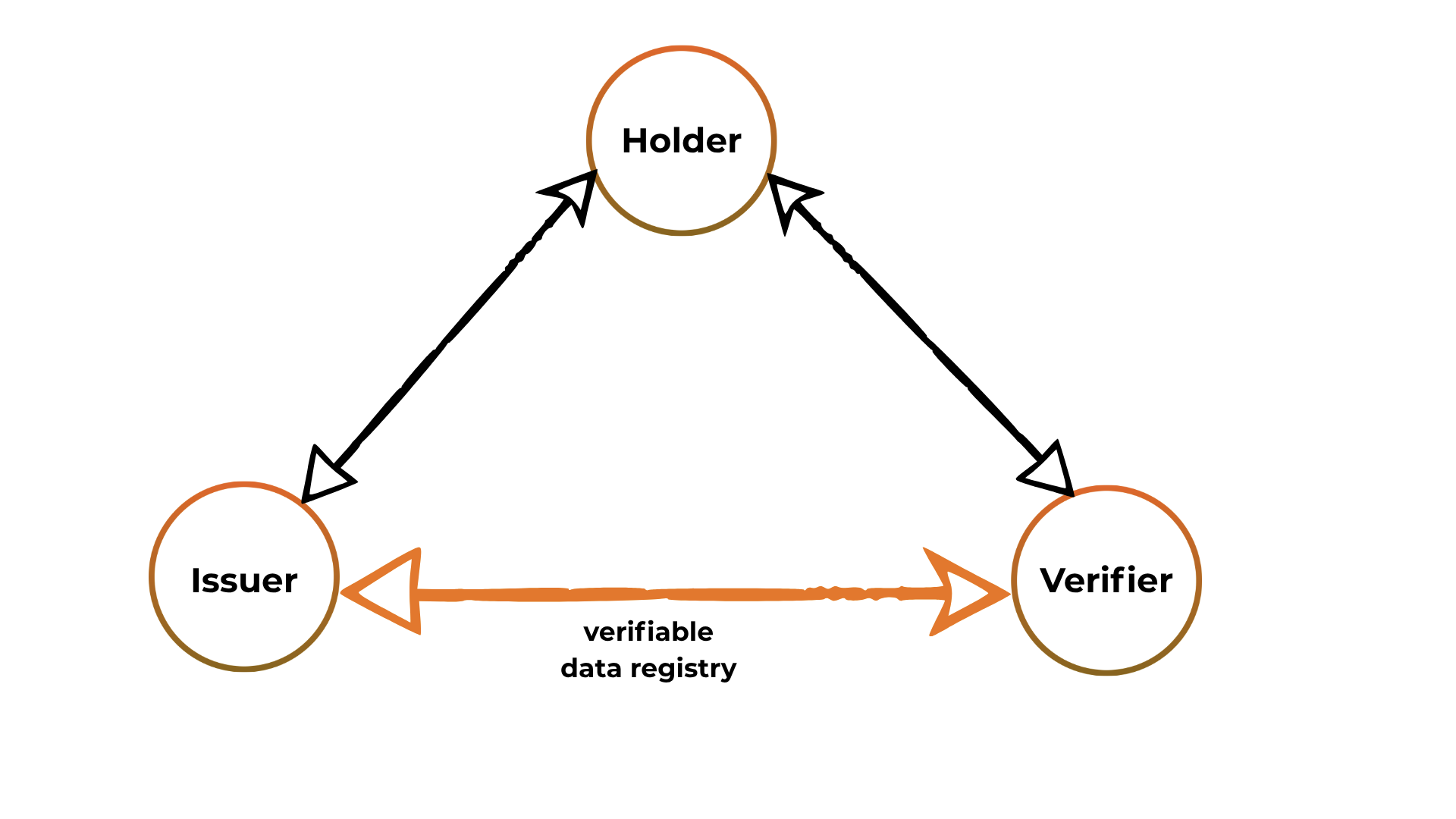
The key difference in this model, compared to traditional systems, is that the verifier does not need to contact or rely on the issuer for verification. Instead, it trusts a decentralized, tamper-proof registry to verify the credential — following W3C standards — where verification happens using a verifiable data registry (such as a blockchain or distributed ledger).
How VCs Leverage DLT (such as Hedera Hashgraph or blockchain), and DIDs
Verifiable Credentials (VCs), Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT), and Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs) work together to create a trusted, decentralized verification system — where verifiers can confirm credentials without relying on a centralized database or issuer.
DLT (such as Hedera Hashgraph or blockchain) ensures that information is stored in a tamper-proof, cryptographically secure manner. Details such as DIDs and public keys are recorded on the ledger, making the DLT act as a trusted registry for verification.
DIDs (Decentralized Identifiers) are globally unique digital identities that represent a person, organization, or entity without depending on a central authority. Unlike traditional identities, DIDs are fully owned and controlled by the user, allowing them to prove identity, authenticate securely, and receive or claim credentials.
Together, these technologies enable a secure, privacy-preserving, and user-owned digital identity ecosystem.
Note: In general, DLT (such as Hedera Hashgraph or blockchain) does not store personal data such as name, date of birth, address, or the Verifiable Credential itself on the chain. DLTs are public by nature, though private registries are also available. They only store public information used for authenticating and validating credentials. The information stored on the DLT (such as Hedera Hashgraph or blockchain) includes Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs), public cryptographic keys, and credential schemas.
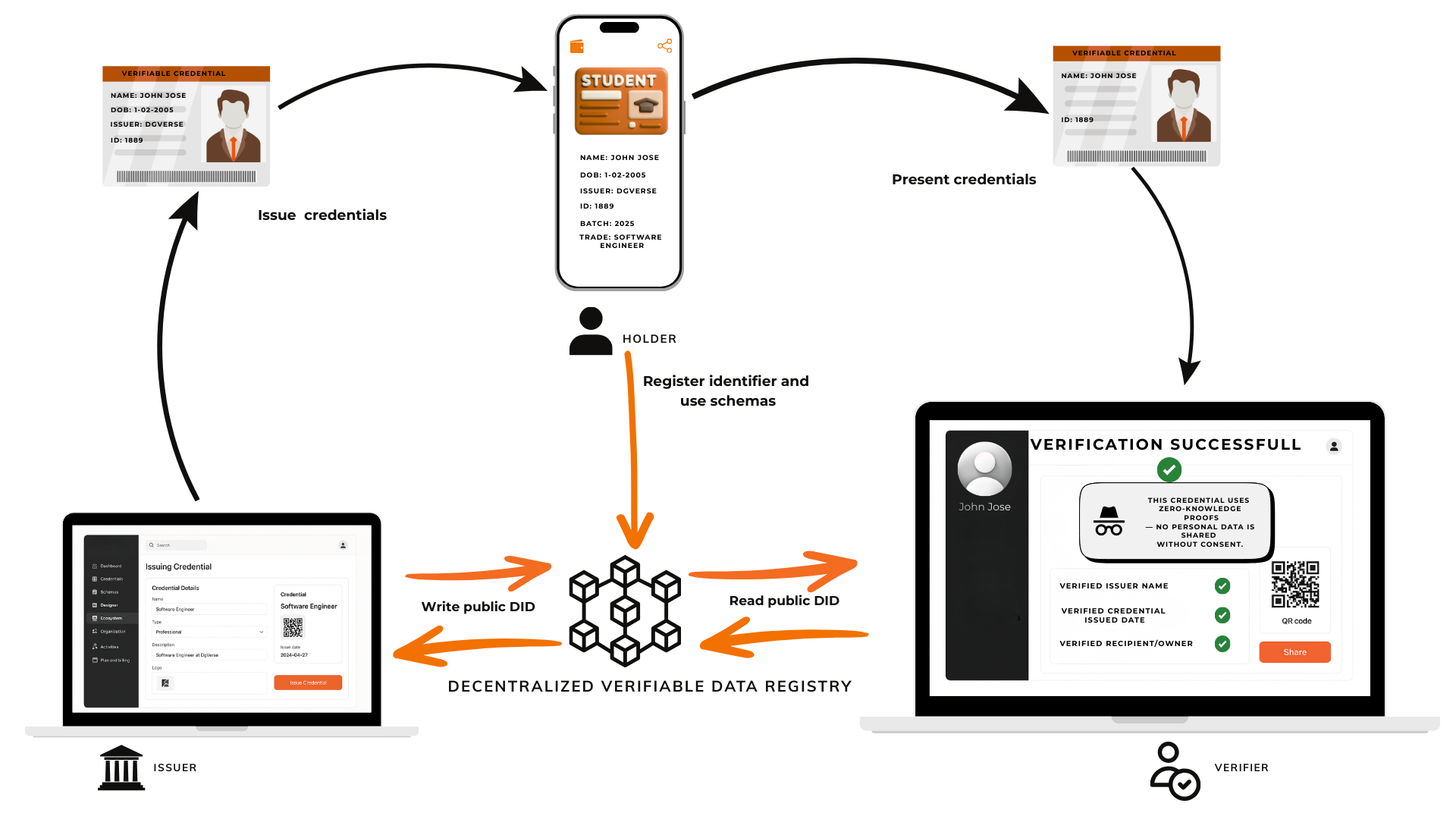
Let's see how this works in a real-world example. Imagine you're part of a large digital ecosystem — like Wakanda City. After completing your KYC, the Wakanda government issues you a Verifiable Credential (VC) proving your membership in the city's ecosystem. Which can be claimed and stored in a digital wallet.
When the VC is issued, the issuer (Wakanda) signs the credential using its private key and links it to your DID (Decentralized Identifier). The issuer itself also has a DID, proving its own identity.
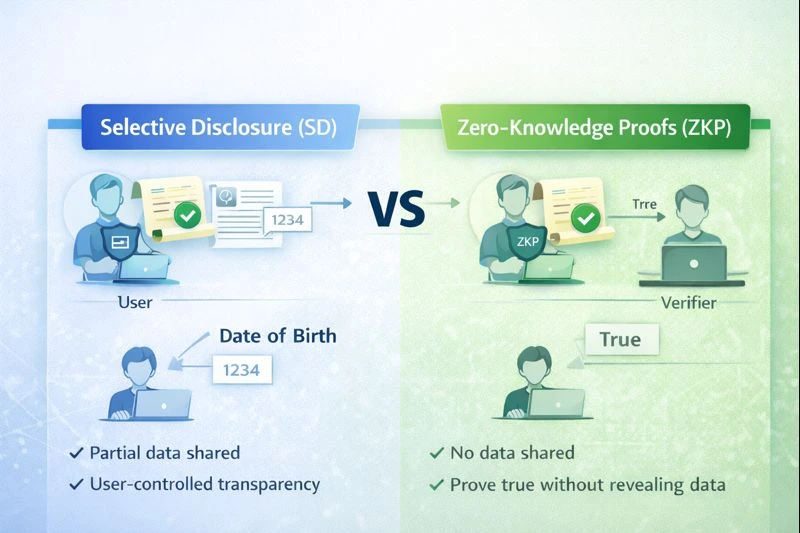
Now, as a citizen, you can access the entire Wakanda ecosystem. Suppose you visit a Wakanda library — when asked for ID, you present your credential to the verifier (the library). The verifier scans and verifies the credential's signature against Wakanda's public key, which is stored on a public, tamper-proof DLT (such as Hedera Hashgraph or blockchain) registry — all without contacting the issuer. If the key matches, the verifier confirms the credential is authentic. leveraging Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs), you can even prove your eligibility (e.g., age) without revealing personal details like your name or date of birth. This model applies across various sectors — finance, education, and healthcare — as long as issuers and verifiers operate within a trusted, decentralized, verifiable registry.
Need for Verifiable Credentials
We need a secure and reliable way to share and verify credentials today without losing privacy and with trust that is transparent and global. Traditional credentials present significant challenges that Verifiable Credentials aim to solve.
Key Use Cases of Verifiable Credentials
Education and Training Certification Bodies
Traditional credentials are paper-based or static PDFs, often stored in centralized systems that depend heavily on the issuer. This causes friction in issuance and verification. With VCs, credentials can be issued and verified instantly — globally and securely.
Healthcare Industry
The current healthcare industry faces huge problems in proving the authenticity of health professionals and their related credentials, which causes onboarding delays and administrative friction. With VCs, this can be faster and simpler.
Human Resource Management
Verifying and managing employee credentials, history, and professional licenses and certificates is hard to manage. The current process relies on third-party services for verification, which delays the whole process and creates more friction. This can be eliminated with VCs and trusted decentralized registries between verifiers and issuers.
Supply Chain Management
This is one big industry that has been struggling for centuries with counterfeit goods and items — especially luxury goods. Proof of authenticity and origin still relies on paper and PDF documents, which are easily forged and non-traceable. With VCs, we can build a new ecosystem of trust between buyers, sellers, and traders.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Identity and Access Management is another industry that can be disrupted with the introduction of VCs. Traditional systems rely on centralized authorities that hold our data. With VCs, identities are issued and managed in a decentralized way — allowing organizations to issue identity credentials that can be used to securely log in and access multiple systems without re-registration.
Why It Matters
Enhanced Security and Fraud Prevention
VCs are tamper-proof through cryptography, making them impossible to forge or alter, thereby eliminating fraud and improving trust. By leveraging DLT (such as Hedera Hashgraph or blockchain), authenticity and integrity are ensured.
Fast and Reliable Verification
Credentials can be instantly verified globally, reducing friction and enabling smoother, faster onboarding and verification across different sectors.
Privacy Preservation
Users own their data and can choose what exactly needs to be shared for verification using Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP) and selective disclosure. For example, one can prove being over 18 without revealing their date of birth or name.
User Control and Data Ownership
With SSI and ZKP standards, users retain full control of their data and have the privilege to decide who, when, and what information to share.
Interoperability and Scalability
By leveraging open standards, VCs can be shared and verified globally across different platforms, organizations, and ecosystems — ensuring interoperability without relying on centralized bodies or databases.
Cost Savings
Automating verification with VCs reduces manual effort, minimizes administrative overhead, streamlines onboarding, and lowers costs associated with identity checks, KYC, and credential validation.
Builds Trust and Stronger Relationships
Since Verifiable Credentials are cryptographically signed and cannot be forged, they establish trust and transparency across entities and organizations within an ecosystem.
The future of credentials is not just digital — it's trusted, verifiable and owned by you.
Each credential is proof that tells your story — one that should be owned by you, shareable and verifiable globally with trust, rather than getting lost between systems. We are building this vision — a new layer of digital trust. This shift will usher in a new era for credentials and verification across institutions, governments, and ecosystems, shaping a more trusted digital world.
If you're ready to explore how verifiable credentials can work for your organization, get in touch at DgVerse.